Match each tissue type with an example of its location – Delving into the fascinating world of tissue types and their locations, this article embarks on a journey to uncover the intricate tapestry of human biology. From the delicate linings of our organs to the robust structures that support our bodies, each tissue plays a vital role in maintaining our health and well-being.
As we delve into the diverse array of tissue types, we will explore their unique characteristics and discover the remarkable locations where they reside within the human body.
Epithelial tissue, the protective barrier that lines our organs and glands, forms the outermost layer of our skin and guards the delicate linings of our internal cavities. Connective tissue, the versatile matrix that binds our bodies together, provides support and cushioning, as exemplified by tendons, ligaments, and bones.
Muscle tissue, the engine that powers our movements, ranges from the voluntary control of skeletal muscles to the involuntary contractions of smooth muscles and the rhythmic beating of cardiac muscles. Nervous tissue, the intricate network that governs our thoughts and actions, resides within the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, transmitting electrical impulses that orchestrate our every move.
1. Tissue Types and Their Locations: Match Each Tissue Type With An Example Of Its Location
Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform specific functions in the body. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each tissue type has a unique structure and function, and is found in specific locations within the body.
| Tissue Type | Location |
|---|---|
| Epithelial Tissue | Skin, lining of organs, glands |
| Connective Tissue | Tendons, ligaments, bones |
| Muscle Tissue | Skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, cardiac muscles |
| Nervous Tissue | Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
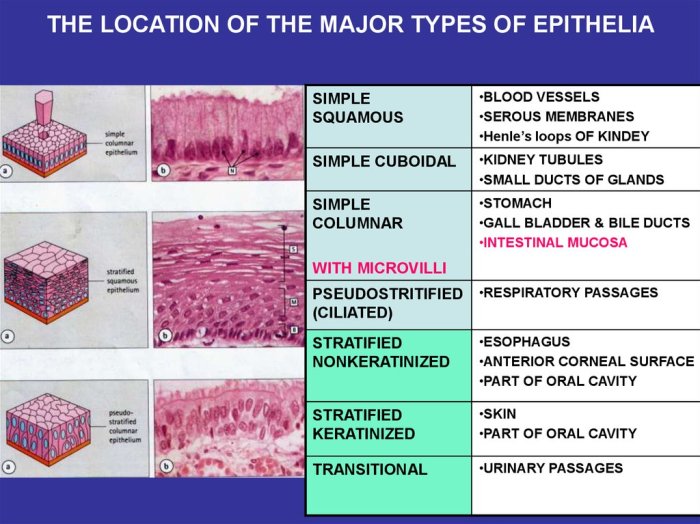
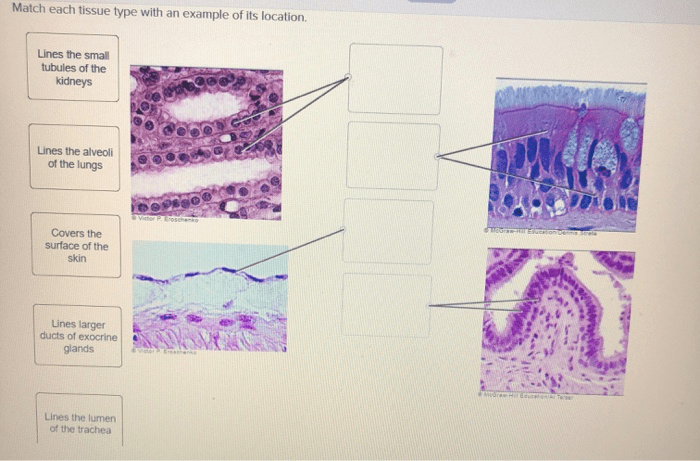
2. Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is the lining of the body’s surfaces, including the skin, the lining of organs, and the glands. It protects the body from the environment, absorbs nutrients, and secretes substances.
Characteristics and Functions of Epithelial Tissue
- Closely packed cells
- Little intercellular space
- No blood vessels
- Protection
- Absorption
- Secretion
Examples of Epithelial Tissue Locations
- Skin
- Lining of organs (e.g., stomach, intestines)
- Glands (e.g., sweat glands, salivary glands)
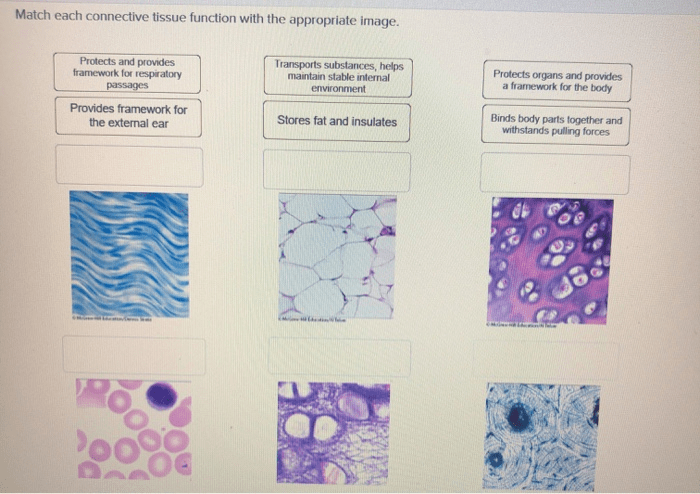
3. Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects the body’s organs and tissues. It is made up of cells embedded in a matrix of fibers and ground substance.
Types of Connective Tissue
- Loose connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone
Functions of Connective Tissue
- Support
- Connection
- Protection
- Storage
- Repair
Examples of Connective Tissue Locations
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Bones
- Cartilage (e.g., in joints, ears)
4. Muscle Tissue

Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It is made up of cells that contain specialized proteins that allow them to contract and relax.
Types of Muscle Tissue
- Skeletal muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
Functions of Muscle Tissue
- Movement
- Support
- Heat production
Examples of Muscle Tissue Locations, Match each tissue type with an example of its location
- Skeletal muscles (e.g., biceps, quadriceps)
- Smooth muscles (e.g., in the stomach, intestines)
- Cardiac muscle (e.g., in the heart)
5. Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is responsible for communication and control in the body. It is made up of cells that can generate and transmit electrical signals.
Structure and Function of Nervous Tissue
- Neurons (nerve cells)
- Glial cells (support cells)
- Communication via electrical signals
- Control of body functions
Examples of Nervous Tissue Locations
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Nerves
FAQ
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue forms a protective barrier, lining organs and glands, and regulating the passage of substances.
Where is connective tissue found?
Connective tissue is widely distributed throughout the body, providing support, cushioning, and binding structures together.
What are the different types of muscle tissue?
There are three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle, each with distinct functions and locations.
What is the role of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue transmits electrical impulses, coordinating communication between different parts of the body and controlling bodily functions.