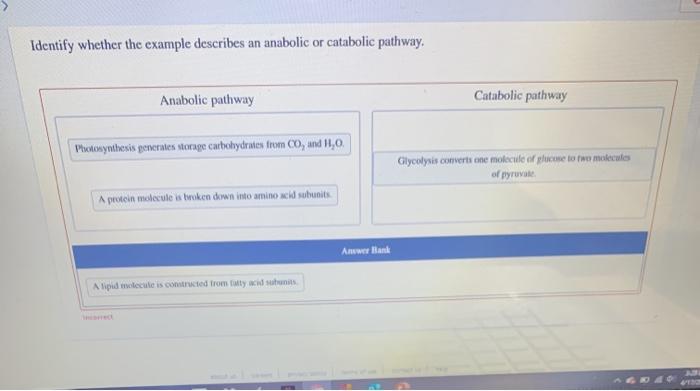
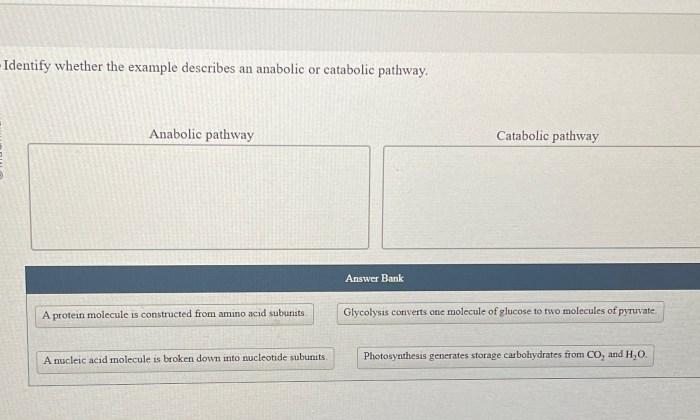
Identify whether the example describes an anabolic or catabolic pathway. – Understanding the intricacies of anabolic and catabolic pathways is paramount in comprehending the fundamental processes that govern cellular metabolism. This guide delves into the distinctive characteristics of these pathways, providing a comprehensive framework for identifying and contrasting their roles in biological systems.
Anabolic pathways, responsible for building and repairing cellular components, stand in stark contrast to catabolic pathways, which break down complex molecules to generate energy. By exploring the defining features of each pathway, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that underpins cellular homeostasis.
Understanding Anabolic and Catabolic Pathways
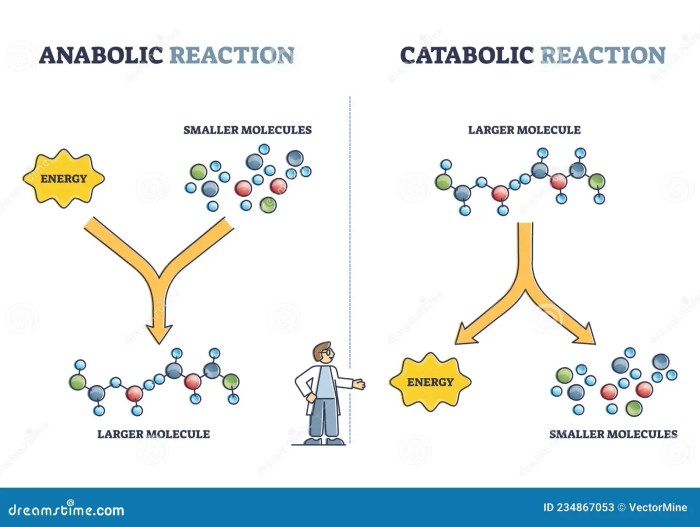
In the realm of metabolism, two fundamental pathways govern the intricate dance of building and breaking down biological molecules: anabolic and catabolic pathways. Anabolic pathways, like skilled architects, construct complex molecules from simpler building blocks, fueling growth and repair. Catabolic pathways, on the other hand, act as dismantlers, breaking down complex molecules into smaller components to generate energy and essential precursors.
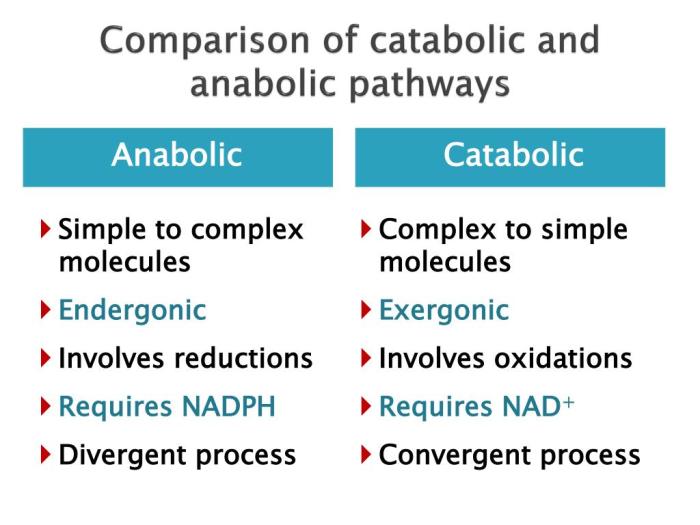
The distinction between these pathways lies in their contrasting purposes and the direction of their chemical reactions. Anabolic pathways, driven by the input of energy, synthesize molecules, increasing their complexity and energy content. Catabolic pathways, in contrast, release energy by breaking down molecules, reducing their complexity and energy content.
Top FAQs: Identify Whether The Example Describes An Anabolic Or Catabolic Pathway.
What are the key differences between anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways synthesize complex molecules, requiring energy input, while catabolic pathways break down complex molecules, releasing energy.
How can I identify an anabolic pathway?
Anabolic pathways typically involve the formation of new chemical bonds, leading to an increase in molecular complexity and energy storage.