What is the ridged outer layer of a plant cell? This question delves into the fascinating realm of plant biology, where we explore the intricate structure and vital functions of the cell wall, the protective and supportive barrier that surrounds every plant cell.
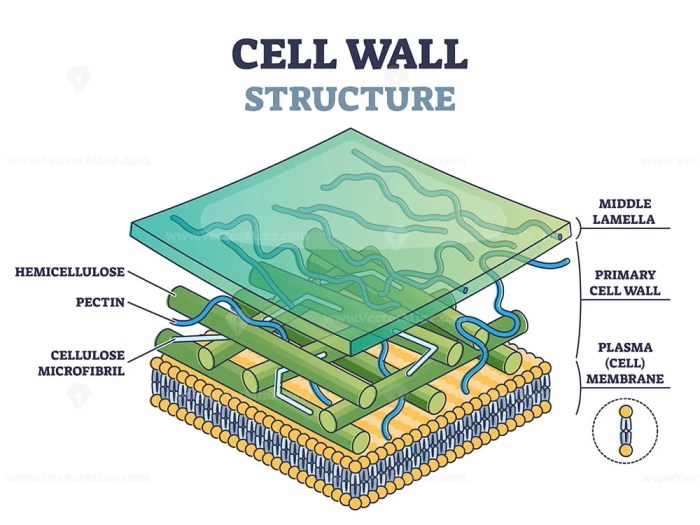
Composed primarily of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, the cell wall provides rigidity, shape, and protection to the cell. It plays a crucial role in water and nutrient transport, facilitating the movement of essential substances into and out of the cell.
Furthermore, the cell wall undergoes modifications in different plant tissues, contributing to their unique properties and functions.
Define the Ridged Outer Layer of a Plant Cell
The ridged outer layer of a plant cell is the cell wall, a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides protection, shape, and support.
Components of the Cell Wall
Cellulose, What is the ridged outer layer of a plant cell
Cellulose is the primary structural component of the cell wall, providing strength and rigidity. It is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules linked together in long chains.
Hemicellulose
Hemicellulose is a branched polysaccharide that cross-links cellulose chains, adding flexibility and elasticity to the cell wall.
Pectin
Pectin is a complex polysaccharide that fills the spaces between cellulose and hemicellulose, providing adhesion and hydration.
Lignin
Lignin is a complex polymer that strengthens the cell wall, especially in secondary cell walls, providing rigidity and resistance to water.
Functions of the Cell Wall: What Is The Ridged Outer Layer Of A Plant Cell
Protection
The cell wall protects the cell from mechanical damage, pathogens, and dehydration.
Cell Shape and Rigidity
The cell wall maintains the shape of the cell and provides rigidity, preventing the cell from bursting due to osmotic pressure.
Water and Nutrient Transport
The cell wall regulates the flow of water and nutrients into and out of the cell.
Cell Wall Modifications
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are channels in the cell wall that allow communication and transport of molecules between adjacent cells.
Cell Wall Enzymes
Cell wall enzymes, such as pectinases and cellulases, play a role in cell growth, development, and defense.
Applications of Cell Wall Research
Biofuel Production
Cell wall components, such as cellulose, are used as feedstock for biofuel production.
Agriculture
Cell wall engineering can improve crop yield and resistance to pests and diseases.
Paper and Textile Industries
Cell wall components are used in the production of paper, textiles, and other products.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of the cell wall?
The primary function of the cell wall is to provide structural support and protection to the plant cell.
What is the main component of the cell wall?
Cellulose is the main component of the cell wall, providing strength and rigidity.
How does the cell wall contribute to water transport?
The cell wall contains channels and pores that facilitate the movement of water and nutrients into and out of the cell.